Governance Frameworks for Biotechnologies Beyond Conventional Containment

Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 2 
Marken JP * , Halleran AD * , Rahman A, Odorizzi L, LeFew MC, Golino CA, Kemper P, Saha MS. PLoS One, 2016 Dec 15.
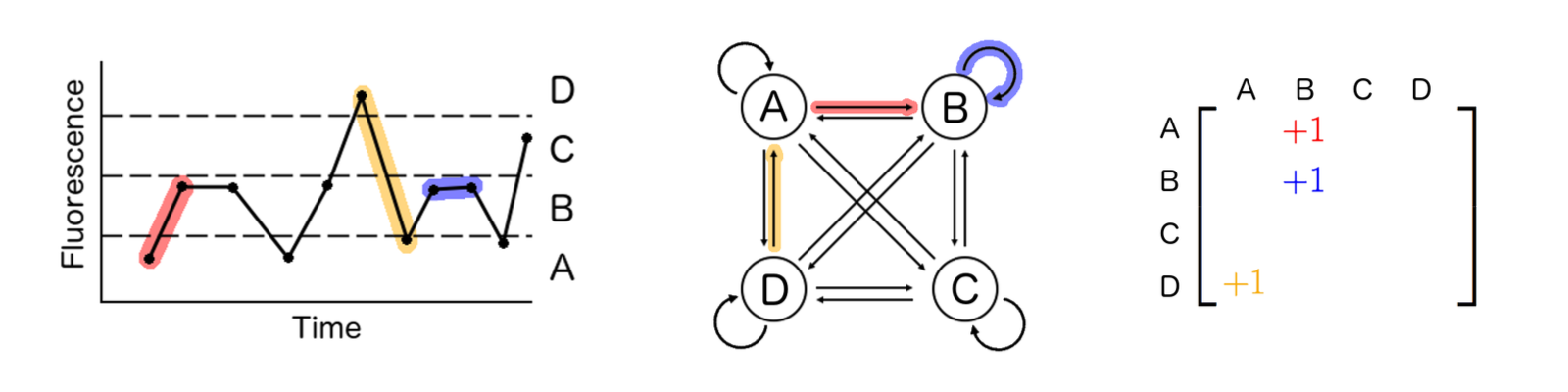
Unlike mature neurons, Xenopus laevis neural progenitors do not display stereotyped spiking behavior in their calcium dynamics, precluding the use of spike-counting algorithms to analyze time-series datasets. Jointly with Andy Halleran, we developed an algorithm that represents the calcium dynamics as a Markov process and calculates the entropy associated with the corresponding transition matrix. Our method was able to separate the calcium activity datasets from developmentally-distinct stages of progenitor cells more strongly than conventional methods. [Link] [pdf]
Marken JP * , Xiao F * , Murray RM. bioRxiv Preprint, 2020 Feb 19.
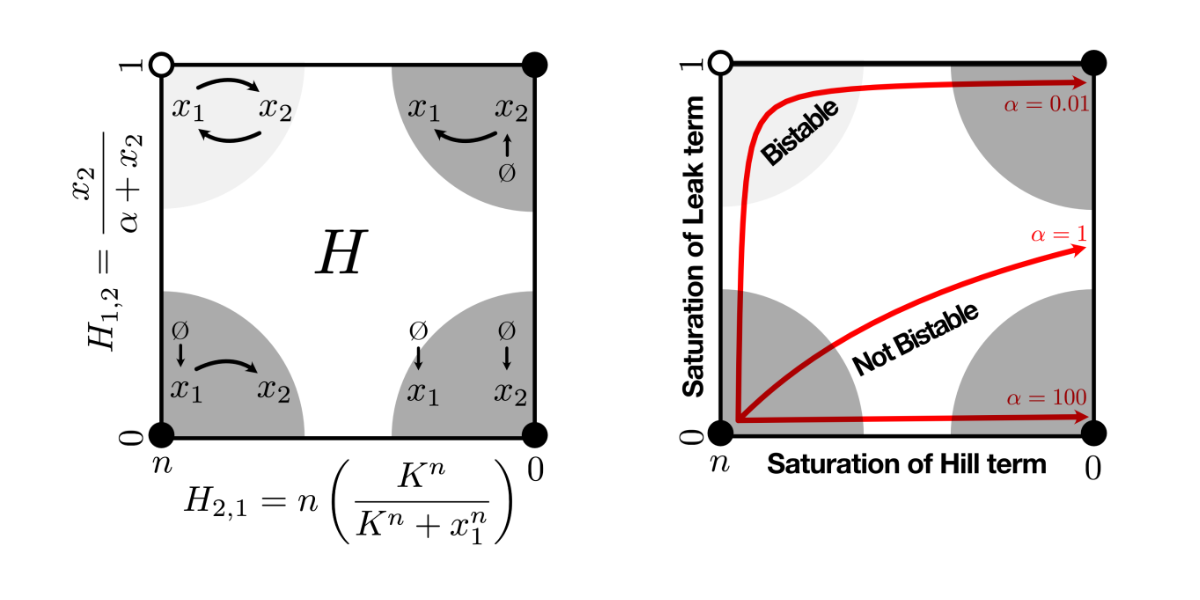
When synthetic biologists design and analyze genetic circuits, the mathematical tools and conceptual frameworks that we use typically come from other disciplines, like engineering and computer science. But what would it look like to have a mathematical theory that was specifically developed for biomolecular systems? Jointly with Fang Xiao, we propose just such a framework, focusing on the ubiquitous presence of saturation in biomolecular reactions. Our central insight is that a genetic circuit can be approximated by a set of simpler circuits depending on the system's saturation state, and by analyzing these simpler circuits, we find that dynamic properties like bistability and oscillations can actually be encoded at a more fundamental, structural level than could be seen with conventional analysis approaches. [Link] [pdf]
Marken JP, Murray RM. Nature Communications, 2023 Apr 24.
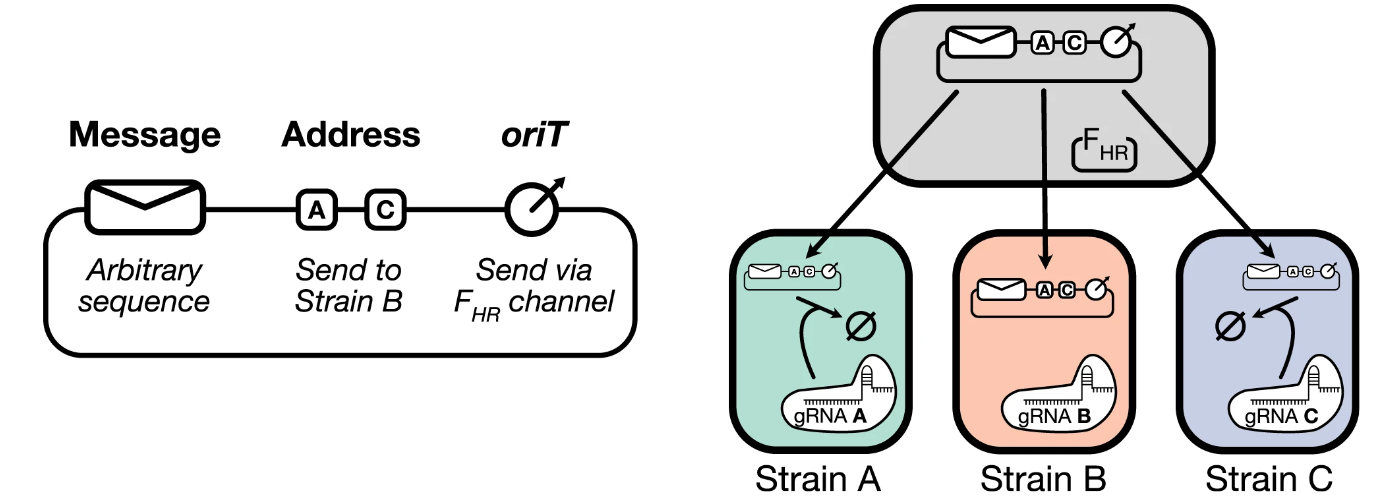
By encoding messages into mobile DNA elements, one can massively scale up the bandwidth of intercellular communication channels in engineered bacterial populations. Ortiz and Endy first implemented this insight in 2012, but after over a decade there has still been little adoption of DNA-based communication by the wider field. Here I developed a modular and scalable framework for DNA-based communication that leverages its unique property of dynamic message mutability to enable messages to be addressed to specific recipients in a population. Furthermore, these messages are editable in situ by the cells themselves, allowing the system to dynamically reprogram the flow of information within itself in response to control signals. [Link] [pdf]
Jones EM *, Marken JP *, Silver PA. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024 Jan 22.
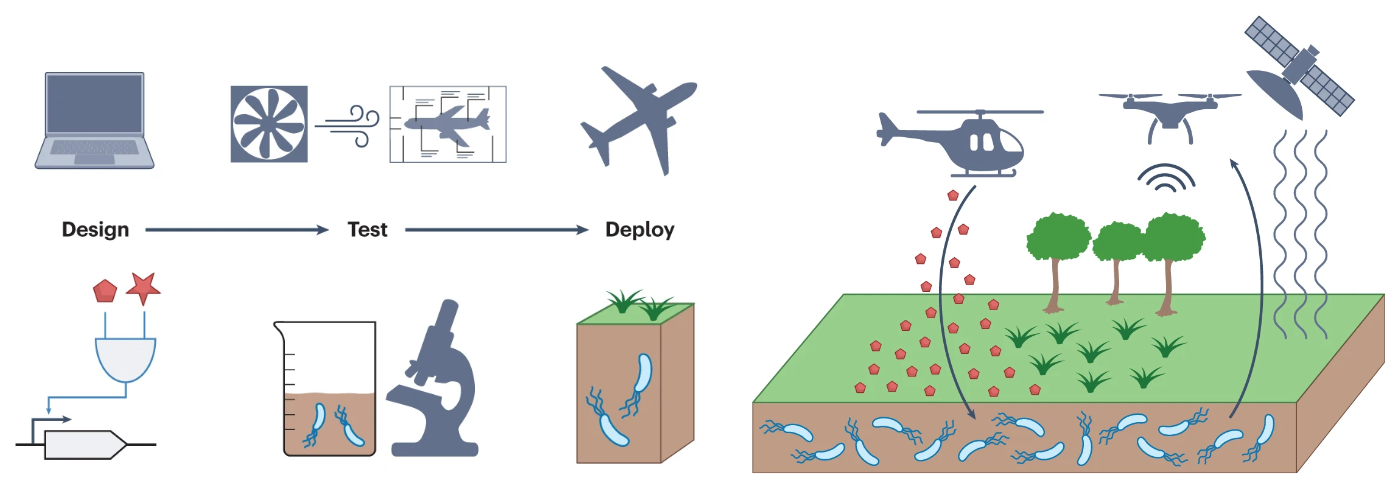
Engineered microbes have great potential for addressing the many sustainability challenges that we face today. In this review, Ethan Jones and I develop an organizing framework for the various classes of applications of synthetic biology for sustainability. We use the property of environmental interfacing, the extent to which the engineered microbe is exposed to the natural environment in its deployment context, to categorize applications areas into three domains: Factory, Farm, and Field. This framework reveals common principles and challenges shared by application areas that are typically viewed as disparate, revealing important research directions that cross disciplinary boundaries. [Link] [pdf]
Marken JP, Prator ML, Hay BA, Murray RM. bioRxiv Preprint, 2026 Feb 2.
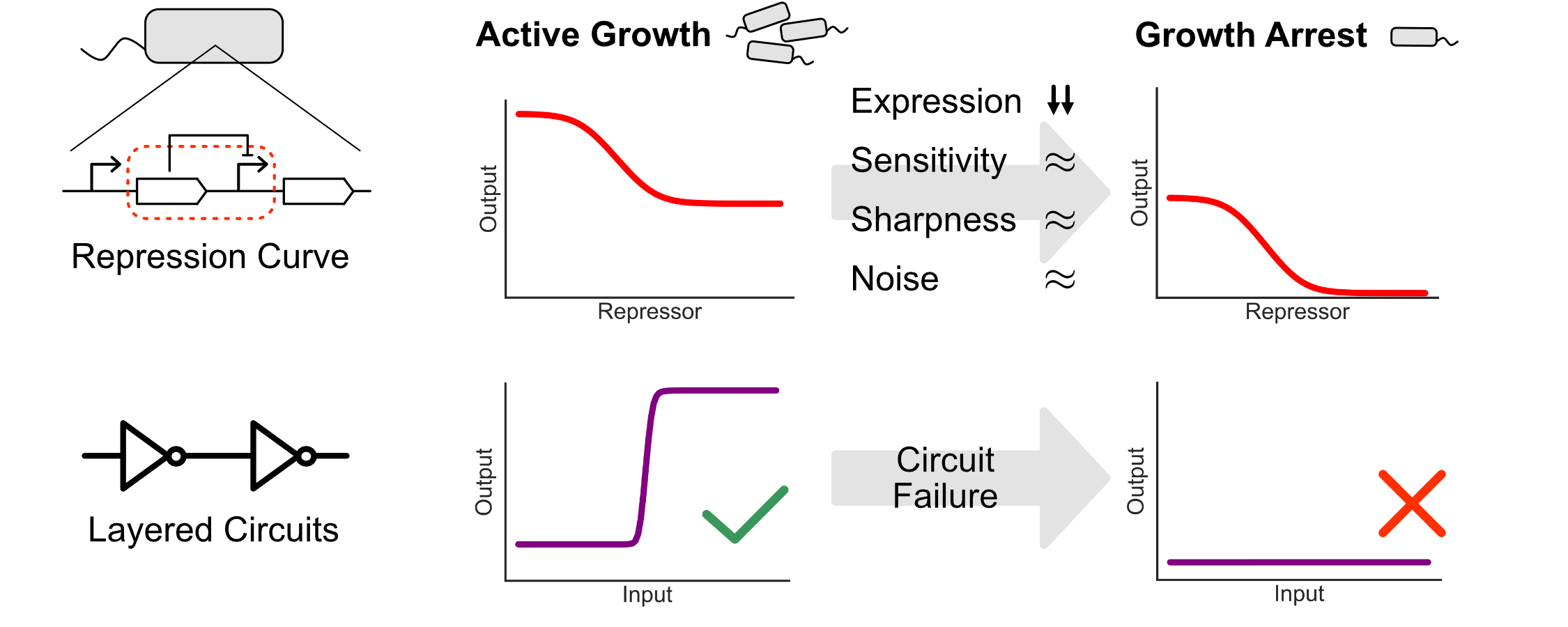
Many of the application areas where synthetic biology could have the greatest impact involve the release of engineered microbes into environmental contexts like the human gut, agricultural croplands, or polluted environments. However, we know very little about how the behavior of engineered genetic circuits would change under such environmental conditions. In this work, we systematically measured how the performance of a common engineered genetic component, a repression-based NOT gate, varies between two cellular growth conditions: active growth and growth arrest. We found that growth arrest imposes dramatic reductions in gene expression strength that make standard circuit design frameworks fail. However, we also found that these impacts were tied to changes in a single performance parameter, which would resolve these failures if corrected. This work therefore exposes the limits of current genetic design paradigms for environmental applications while also revealing research directions for overcoming these limits. [Link] [pdf]
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.